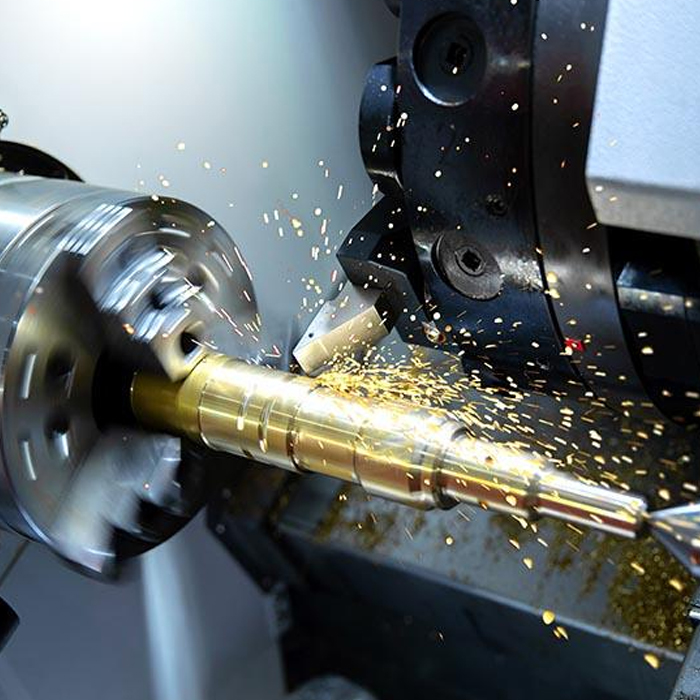
What is the main purpose of CNC machines?
1. What is a CNC Machine?
A Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machine is a computerized manufacturing tool that utilizes a pre-programmed computer software for directing the movement of factory machinery and tools. Essentially, a CNC machine is a versatile and powerful piece of equipment that can automate complex tasks, such as cutting, milling, drilling, or shaping, with high precision and efficiency. By automating the manufacturing process, CNC machines can significantly reduce human intervention, minimize errors, and decrease lead times.
2. Types of CNC Machines
There are several types of CNC machines, with each catering to specific industries and applications:
CNC Milling Machines: These machines utilize computerized controls to direct the movement of cutting tools, effectively removing material from workpieces to create desired shapes and designs.
CNC Lathes: These machines employ the CNC technology for accurately turning workpieces to create parts with rotational symmetry, such as axles or screws.
CNC Routers: Typically used in woodworking and metalworking, CNC routers excel at cutting and shaping materials into intricate and detailed patterns.
CNC Plasma Cutters: These machines employ plasma cutting technology for precisely cutting and shaping materials like steel and other metals.
CNC Laser Machines: These machines use focused light beams to cut and engrave a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood.
3. What is the main purpose of CNC machines?
The primary purpose of CNC machines is to automate the manufacturing process and ensure precision, consistency, and efficiency in producing parts and components across a wide range of industries. CNC machines can execute complex designs and high levels of detail with minimal human intervention, making them indispensable in modern production lines. Some of the key objectives behind using CNC machines include:
3.1 Enhancing Precision and Accuracy
CNC machines are renowned for their ability to produce parts with exceptional precision and accuracy, a vital consideration in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. The use of pre-programmed CAD/CAM software allows for even the most intricate and complicated designs to be brought to life, with tight tolerances and minimal errors.
3.2 Increasing Production Efficiency
The automation of manufacturing tasks translates into increased production efficiency, as CNC machines can operate around the clock and produce components at a rapid pace. These machines can complete multiple operations in a single setup, reducing time-consuming manual intervention and eliminating the need for recalibration between tasks.
3.3 Ensuring Consistency and Quality
CNC machines ensure that each part produced is consistent with the design specifications, guaranteeing repeatable and high-quality outputs. This uniformity is vital in mass production scenarios and industries in which part interchangeability is crucial.
3.4 Minimizing Waste and Material Usage
By optimizing cutting paths and reducing human error, CNC machines can minimize material waste and make the most of raw materials. The efficient use of resources contributes to cost savings and promotes sustainability in the manufacturing process.
4. Advantages of CNC Machines
Apart from their main purpose, CNC machines offer several additional benefits:
Reduced labor costs: The high degree of automation results in less manual labor, hence lowering labor expenses.
Improved safety: The CNC technology enhances workplace safety by reducing human interaction with dangerous machinery and tasks.
Increased design flexibility: CNC machines enable quick and easy adjustments to part designs, providing the flexibility to accommodate design changes without significant downtime.
5. Future Trends for CNC Machines
The future trends for CNC machines include:
Industry 4.0 Integration: As manufacturing becomes increasingly digital and interconnected, CNC machines are expected to play a significant role in the Industry 4.0 revolution.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and ML technologies can further optimize CNC machine efficiency and accuracy by enabling adaptive designs and real-time adjustments.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): CNC machines may increasingly work alongside cobots, blurring the lines between automation and human collaboration in production processes.
6. Factors Affecting CNC Machine Prices
Several factors can influence the price of a CNC machine:
Type and Size: The specific type and size of the CNC machine, depending on its capabilities and applications, can significantly impact its cost.
Complexity and Features: The level of complexity and the variety of features offered can also affect the price, as more advanced machines often come with a premium price tag.
Manufacturer and Brand: Well-established and reputable manufacturers may charge higher prices due to their reputation for quality products and after-sales services.
7. What to Consider When Buying a CNC Machine
When purchasing a CNC machine, take the following factors into account:
Your Specific Needs: Evaluate your production requirements, the types of materials you will be working with, and the level of precision needed.
Budget Constraints: Determine a realistic budget, keeping in mind the initial investment, training costs, maintenance, and software expenses.
Compatibility With Existing Setup: Ensure the CNC machine you select is compatible with your current production line and can be efficiently integrated without causing major disruptions.
8. Conclusion
CNC machines serve as the backbone of modern manufacturing by automating complex tasks, enhancing precision, increasing production efficiency, and ensuring consistent quality across various industries. As the main purpose of CNC machines becomes increasingly relevant in the face of evolving manufacturing trends, businesses must adopt this technology to remain competitive and streamline their production processes. By understanding the key factors that contribute to a CNC machine's cost, performance, and compatibility, manufacturers can confidently invest in the right equipment to achieve their specific production goals.